Is Your Brain Causing Your Chronic Pain?
You would have every right to be offended if someone said your pain was all in your head. But the truth is, 100% of pain is constructed entirely in the brain. This doesn’t mean your pain is any less real – your brain initiates what your body feels, and in case of chronic pain, your brain is what perpetuates it.
Pain is a complicated warning system to protect you from harm. When you stub your toe, your peripheral nervous system sends signals from your toe to your brain, which then decides how much danger there is. If it decides the signals are worth paying attention to, the brain turns the pain volume up until the problem is resolved; if the brain decides there is not much danger, the pain is put on mute.
Chronic pain is like a fire alarm that is so hyper-sensitive, it goes off every time you cook
This system works pretty well for acute pain, like an injured toe. But in chronic conditions like osteoarthritis (OA), where there’s no quick fix for, say, cartilage loss in the knee, the parts of the brain that send and receive danger signals become more sensitive over time. Scientists say the more the brain processes pain, the more hyper-sensitive it gets until it is always on high alert.
Pain is the brain's danger alert system – much like a fire alarm going off when it senses smoke. But chronic pain is like a fire alarm that is so hyper-sensitive, it goes off every time you cook anything in your kitchen.
When the brain senses danger, it produces pain in the area it thinks is the cause of the danger. As an example - when you step on a nail with your bare foot, nerve signals shoot up to your brain to evaluate if this is dangerous. The brain must determine the amount of danger based on many inputs - including the memory of your past experiences with this type of situation. The brain then responds by sending the appropriate intensity of pain signals from the brain to your foot.
A growing understanding of how this happens – and the need to find better alternatives to pain medications – has led to renewed interest in using EEG biofeedback to address the brain dysfunction, NOT the part of the body where you feel the pain. Unlike drugs, EEG biofeedback doesn’t mask or numb chronic pain. Instead, it aims to normalize or reset the brain’s high alert system. This approach can significantly relieve pain without drugs – in some cases, it’s the first time many people get relief.

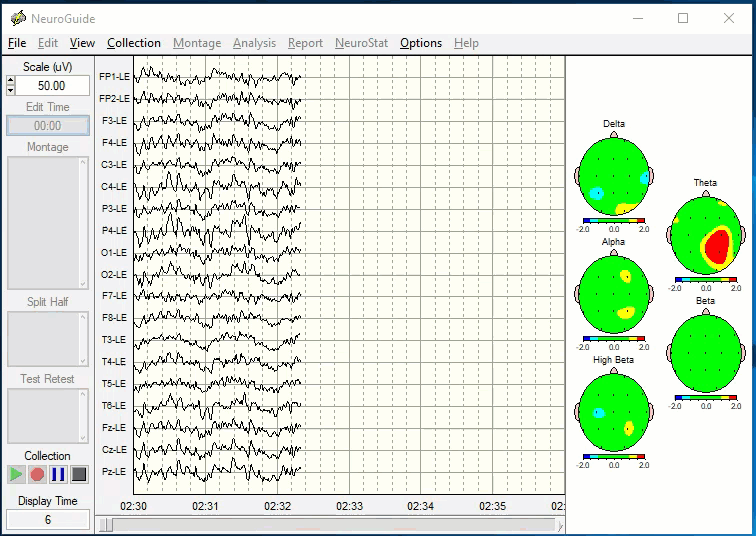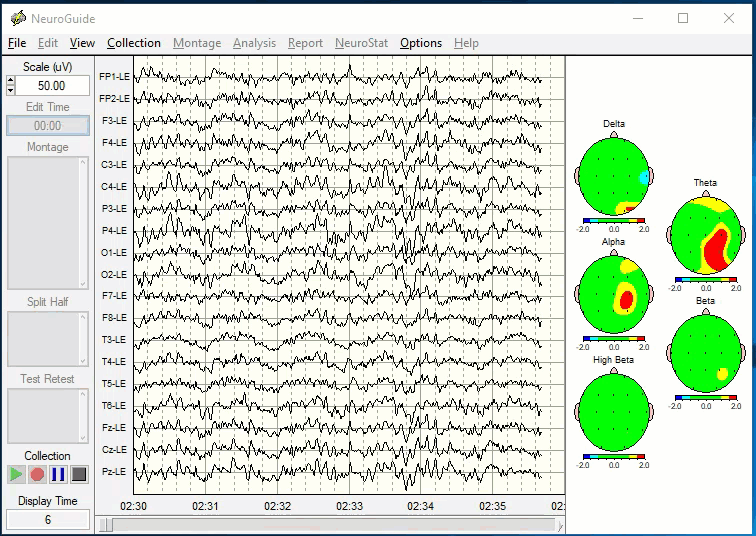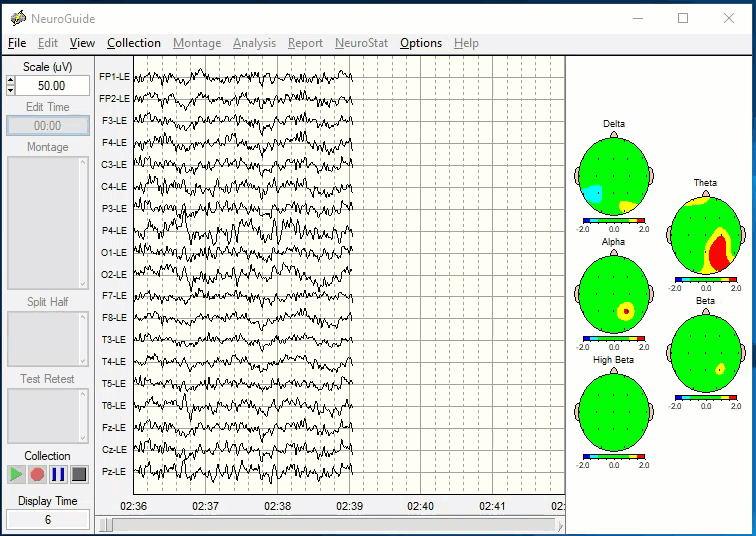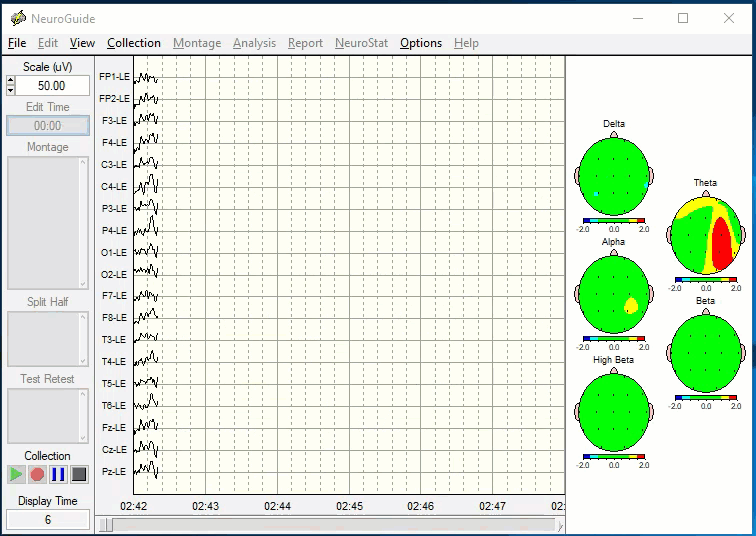
EEG Brain Mapping - Identifying The Source
A brain map takes less than 20 minutes to record and is neither invasive nor painful. You simply wear a cap with 19 sensors that record your brain’s electrical activity while you relax in a chair. It is similar to having an EKG record your heart. It’s as safe as a stethoscope!
EEG brain mapping objectively measures brainwave function. A brain map quantifies regions of the brain that are stuck in high-alert (over-activation). Once we know the location and electrical activity perpetuating the chronic pain, we can use EEG biofeedback therapy and nutritional interventions to return the brain activity to a normal resting state, which in many cases can reset the brain's pain alert system back to normal function and greatly reduce or eliminate chronic pain.

Affordable Simple Actionable
A brain map helps identify specific interventions and treatment plan
Less than 20 minutes to record, non-invasive, no pain (similar to an EKG)
Only $495 for a full brain map and review of findings.
For more information or to schedule a brain map, call or email us at (800) 385-0710 or Info@BrainPerformance.com
3 Southern California locations: Westlake Village, Calabasas & Los Angeles
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an EEG Brain Map?
An EEG brain map objectively measures brain function for people between the ages of 6 and 92. It identifies specific regions of the brain that may be producing too much, or too little electrical activity compared to a controlled, normative database of your same age and gender.
A brain map takes less than 20 minutes to record and is neither invasive nor painful. You simply wear a cap with 19 sensors that record your brain’s electrical activity while you relax in a chair. It is similar to having an EKG record your heart. It’s as safe as a stethoscope!
Is there supporting research
validating EEG brain mapping?
Yes, there are hundreds of research studies on EEG for a wide variety of symptoms, including memory problems, anxiety, depression, traumatic brain injury (TBI), migraines, chronic pain, ADD/ADHD, and processing issues.
EEG is considered the “Gold Standard” in neuroscience for measuring real-time brain function. EEG brain mapping is used by the Department of Defense as well as top institutions including UCLA, UCSD, Stanford and many others.
Will insurance pay for my EEG brain map?
Even though EEG brain mapping has hundreds of research studies, currently, insurance does not pay or reimburse for EEG brain maps. The current insurance model is to prescribe medications solely based on symptoms and history. EEG technology is still a few years away from being considered a “main stream” medical diagnostic tool. However, the Brain Performance Center has recently reduced the price for a full EEG brain map to only $500 (the price for the last 5 years has been $975). This helps make it an affordable, out-of-pocket brain health investment.
How will a brain map help me?
Without an EEG brain map, healthcare providers and therapists rely solely on subjective information like symptoms and history. Neuroscience research has identified 6 different types of brain physiology that can produce anxiety symptoms and 6 others that can produce ADHD symptoms.
Many symptoms can be the result of abnormal brain activity during sleep cycles. Understanding the physiological source is imperative to any treatment plan. EEG brain mapping is the technology that provides an objective assessment to help direct the most effective brain health interventions.
Can I record a brain map even if I
am currently taking medication?
Yes, continue to take your medications prescribed by your doctor. We know how medications affect your brain map and can account for this when reviewing the results.
How do I schedule an EEG brain map?
Call our office at (800) 385-0710 or email us at:
EEG brain mapping is available at our Westlake Village and Los Angeles offices.
Based on my EEG brain map,
will you recommend specific interventions?
An EEG brain map can help identify if your brain function is being affected by nutritional deficiencies, environmental factors, genetic factors, sleep cycle dysfunction, or due to post-concussion activity. If one or more of these are identified, we will recommend specific nutritional interventions, changes to your diet, changes in lifestyle, specific genetic tests, or EEG biofeedback sessions (Neurofeedback) to optimize your brain’s electrical activity.
Who reviews my brain map results with me?
Once your brain map is fully processed, you will have a 1-hour consultation to review your brain map findings with our Director of Neuroscience, Bryan Hixson. Mr. Hixson is one of the leading neuroscience experts in quantitative EEG brain mapping, neurocognitive testing, neurofeedback brain training, and nutritional cellular health.
Mr. Hixson is a brain health expert consultant for AARP’s Staying Sharp platform, serving 38 million members. He is also the Director of Digital Brain Health for Sharecare/DoctorOz.com, the founder and neuroscience director of the Brain Performance Centers, and an EEG brain mapping contractor for the U.S. Army. Additionally, Mr. Hixson is the co-founder of BrainSpan Laboratories, which is used by over 1,000 doctors nationwide. It is the most clinically validated blood spot test available for optimizing fatty acids related to brain health.